Conceptual Rainfall-Runoff Model
Contents
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
import ipywidgets as widgets
from ipywidgets import interact, interactive
from bokeh.plotting import figure, show
from bokeh.io import output_notebook, push_notebook
from bokeh.models import LinearAxis, Range1d, ColumnDataSource
from bokeh.layouts import column, row
import numba
output_notebook()
Conceptual Rainfall-Runoff Model#
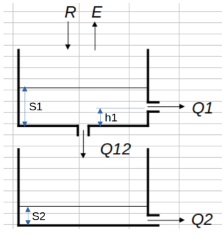
In this notebook, we’re going to set up and calibrate a basic conceptual rainfall-runoff model and calibrate it to some precipitation and runoff data. The conceptual model is as follows:
|
$\(Q_1 = a_1 \cdot (S_1 - h_{1})^{m_1}\)\( \)\(Q_{12} = a_{12} \cdot S_1^{m_{12}}\)\( \)\(Q_2 = a_{2} \cdot S_2^{m_2}\)$ |
Import Climate Data#
We have observations of precipitation and runoff (and estimates of evaporation) at a frequency of 20 minutes. We would like to import them and set up empty vectors to represent the state variables for tank levels and the fluxes.
def initialize_df(df):
# initialize the columns from the input data
cols = ['S1 (mm)', 'Q1 (mm/h)', 'Q12 (mm/h)', 'S2 (mm)', 'Q2 (mm/h)', 'Q1+Q2 (mm/h)']
df.loc[:, cols] = np.nan
# calculate the timestep in minutes
# df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date'].to_numpy())
# get the timestep and convert it to hours
df['dt_hours'] = df['Date'].diff().dt.total_seconds().div(3600)
# for some reason the Date column is unsorted, so sort it
df.sort_values('Date', inplace=True)
return df
raw_data = pd.read_csv('data/data.csv', parse_dates=['Date'], infer_datetime_format=True, dayfirst=True)
df = initialize_df(raw_data)
df.set_index('Date', inplace=True)
df.head()
| Rain (mm/h) | Evap (mm/h) | Runoff (mm/h) | S1 (mm) | Q1 (mm/h) | Q12 (mm/h) | S2 (mm) | Q2 (mm/h) | Q1+Q2 (mm/h) | dt_hours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | ||||||||||
| 1987-09-02 00:20:00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.038 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1987-09-02 00:40:00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.038 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0.333333 |
| 1987-09-02 01:00:00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.038 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0.333333 |
| 1987-09-02 01:20:00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.038 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0.333333 |
| 1987-09-02 01:40:00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.038 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0.333333 |
# this will check if any value in any row is null (i.e. NaN)
# df[df[['Rain (mm/h)', 'Evap (mm/h)', 'Runoff (mm/h)']].isnull().any(axis=1)]
# plot_cols = [c for c in df.columns if c not in ['dt', 'Date']]
p_label = 'Rain (mm/h)'
q_label = 'Runoff (mm/h)'
e_label = 'Evap (mm/h)'
p = figure(title='Observed Precipitation and Runoff',
x_axis_type='datetime', width=800, height=400)
p.line(df.index, df[q_label], line_width=2,
legend_label=q_label, color='dodgerblue')
p.line(df.index, df[e_label], line_width=2,
legend_label=e_label, color='orange')
p.xaxis.axis_label = 'Date'
p.yaxis.axis_label = q_label
p.extra_y_ranges = {"precip": Range1d(df[p_label].max(), 0)}
# data is in 20 minute intervals, and time is in milliseconds,
# so set width to 3.6E6 / 3
precip = p.vbar(
x=df.index,
top=0,
bottom=df[p_label],
width=20 * 60E3,
y_range_name='precip',
legend_label=p_label,
alpha=0.5,
color='lightseagreen',
)
precip.level = 'underlay'
p.add_layout(LinearAxis(axis_label=p_label, y_range_name='precip'), "right")
show(p)
def update_df():
# if you are working in Jupyter lab, you can import the data just once.
# However, there might be issues later on if you are updating the dataframe in
# such a way that values from another iteration interfere.
# it may be a case of just running a modified version of the 'initialize_df'
# function where you just reset the desired columns to nan. This won't take as much
# time as reading the csv and converting the Date column to pandas datetime type.
# df = initialize_df(pd.read_csv('data/data.csv', parse_dates=['Date'], dayfirst=True))
# set_initial rain and evap as zero
rain_0, evap_0 = 0, 0
for i in range(0, len(df)):
if i == 0:
this_S1 = S1_init.value
this_S2 = S2_init.value
else:
# get the timestep and convert it to hours
dt = df.at[i, 'dt_hours']
rain = df.at[i - 1, 'Rain (mm/h)']
evap = df.at[i - 1, 'Evap (mm/h)']
q1 = df.at[i - 1, 'Q1 (mm/h)']
q12 = df.at[i - 1, 'Q12 (mm/h)']
q2 = df.at[i - 1, 'Q2 (mm/h)']
S1 = df.at[i - 1, 'S1 (mm)']
S2 = df.at[i - 1, 'S2 (mm)']
# since our dt is in hours and fluxes in mm/h
# multiply by the timestep to get the sub-hourly fluxes
delta_q1 = (rain - evap - q1 - q12) * dt
# if i < 20:
# print(f'@dt={dt} delta q1 = {delta_q1:.3f}, rain={rain:.1f}, evap={evap:.1f}, q1={q1:.2f}, q12={q12:.2f}')
this_s1 = max(0, S1 + delta_q1)
delta_q2 = (q12 - q2) * dt
this_s2 = max(0, S2 + delta_q2)
# set reservoir levels for the current timestep
df.at[i, 'S1 (mm)'] = this_S1
df.at[i, 'S2 (mm)'] = this_S2
# set flows for the current timestep based on current levels
df.at[i, 'Q1 (mm/h)'] = a1.value * (this_S1 - h1.value)**m1.value
df.at[i, 'Q12 (mm/h)'] = a12.value * (this_S1)**m12.value
df.at[i, 'Q2 (mm/h)'] = a2.value * (this_S2)**m2.value
df.at[i, 'Q1+Q2 (mm/h)'] = df.at[i, 'Q1 (mm/h)'] + df.at[i, 'Q2 (mm/h)']
return df
Interactive Inputs#
@numba.jit(nopython=True)
def update_states_vectorized(rain, evap, dt, a1, m1, h1, a12, m12, a2, m2, S1_init, S2_init):
# df = initialize_df(pd.read_csv('data/data.csv', parse_dates=True, infer_datetime_format=True))
# for jit compiling, we need to initialize empty vectors
# for each of the input columns from the pandas method
s1, s2 = np.empty(len(rain)), np.empty(len(rain))
q1, q2 = np.empty(len(rain)), np.empty(len(rain))
q12 = np.empty(len(rain))
q_tot = np.empty(len(rain))
# set initial reservoir and outflow values
s1[0] = S1_init
s2[0] = S2_init
q1[0] = 0 if s1[0] <= h1 else (a1 * (s1[0] - h1)**m1 ) * dt[1]
q12[0] = (a12 * (s1[0])**m12) * dt[1]
q2[0] = (a2 * s2[0]**m2) * dt[1]
q_tot[0] = q1[0] + q2[0]
for i in range(1, len(rain)):
q1_balance = (rain[i-1] - evap[i-1] - q1[i-1] - q12[i-1]) * dt[i]
this_S1 = max(0, s1[i - 1] + q1_balance)
delta_q2 = (q12[i - 1] - q2[i - 1]) / dt[i]
this_S2 = max(0, s2[i - 1] + delta_q2)
s1[i] = this_S1
s2[i] = this_S2
q1[i] = 0 if this_S1 <= h1 else (a1 * (this_S1 - h1)**m1) * dt[i]
q12[i] = 0 if this_S1 <= 0 else (a12 * (this_S1)**m12) * dt[i]
q2[i] = 0 if this_S2 <= 0 else (a2 * this_S2**m2) * dt[i]
q_tot[i] = q1[i] + q2[i]
return s1, s2, q1, q2, q12, q_tot
def vectorized_df_update(a1, m1, h1, a12, m12, a2, m2, S1_init, S2_init):
p_label = 'Rain (mm/h)'
e_label = 'Evap (mm/h)'
rain = df[p_label].to_numpy()
evap = df[e_label].to_numpy()
dt = df['dt_hours'].to_numpy()
s1, s2, q1, q2, q12, q_tot = update_states_vectorized(rain, evap, dt, a1, m1, h1, a12, m12, a2, m2, S1_init, S2_init)
df['S1 (mm)'] = s1
df['S2 (mm)'] = s2
df['Q1 (mm/h)'] = q1
df['Q2 (mm/h)'] = q2
df['Q12 (mm/h)'] = q12
df['Q1+Q2 (mm/h)'] = q_tot
return df
def plot_model(a1, m1, h1, a12, m12, a2, m2, S1_init, S2_init):
# df = update_df()
df = vectorized_df_update(a1, m1, h1, a12, m12, a2, m2, S1_init, S2_init)
source = ColumnDataSource(df)
q_label = 'Runoff (mm/h)'
sim_label = 'Q1+Q2 (mm/h)'
fig = figure(width=800, height=300, x_axis_type='datetime',
title='Observed vs. Simulated Runoff')
# Plot Measured vs. Simuilated Runoff
fig.line('Date', q_label, color='dodgerblue', line_width=2,
legend_label='Observed', source=source)
fig.line('Date', sim_label, color='navy', line_width=2,
line_dash='dashed', legend_label='Simulated',
source=source)
fig.yaxis.axis_label = 'Runoff (mm/h)'
# Tank 1 and Tank 2 flow plot
f1 = figure(title='Tank 1 and 2 Flow', width=800, height=150,
x_axis_type='datetime')
f1.line('Date', 'Q1 (mm/h)', legend_label='Tank 1',
line_width=2, color='purple', source=source)
f1.line('Date', 'Q2 (mm/h)', legend_label='Tank 2',
line_width=2, color='navy', source=source)
f1.yaxis.axis_label = 'Runoff (mm/h)'
# Regression Plot
f2 = figure(width=400, height=450, title="Measured vs. Simulated Regression")
f2.circle('Runoff (mm/h)', 'Q1+Q2 (mm/h)',
source=source)
# drop NaN values for Least-Squares fit
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# Best-fit line for regression plot
fit = np.polyfit(df['Runoff (mm/h)'], df['Q1+Q2 (mm/h)'], 1)
x = np.linspace(df['Runoff (mm/h)'].min(), df['Runoff (mm/h)'].max(), 100)
y = [fit[0] * e + fit[1] for e in x]
f2.line(x, y, color='red', line_dash='dashed')
# calculate the R^2 and the NSE
df['square_diff_Q1_Q2'] = (df['Runoff (mm/h)'] - df['Q1+Q2 (mm/h)'])**2
# set a lower limit value to avoid divide by zero errors
df = df[(df['Q1+Q2 (mm/h)'] != 0) & (df['Runoff (mm/h)'] != 0)].copy()
df['log_square_diff_Q1_Q2'] = (np.log(df['Runoff (mm/h)']) - np.log(df['Q1+Q2 (mm/h)']))**2
df['log_square_diff_Q1_Q2'] = df[np.isfinite(df['log_square_diff_Q1_Q2'])]['log_square_diff_Q1_Q2']
nse = 1 - df['square_diff_Q1_Q2'].mean() / np.var(df['Runoff (mm/h)'])
# log_nse = df['log_square_diff_Q1_Q2'].mean() / np.var(df['Runoff (mm/h)'])
performance_str = f'Sim. vs. Obs Regression (NSE={nse:.2f})'
f2.title = performance_str
# print(performance_str)
layout = row(column(fig, f1), f2)
show(layout)
# plt.annotate(performance_str, xy=(0, 0),
# xytext=(5, 340),
# textcoords="offset points",
# ha='left', va='center',
# color='black', weight='bold',
# clip_on=True)
from ipywidgets import TwoByTwoLayout, interactive_output, HBox
from IPython.display import display
a1 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=0.5, step=0.01, value=0.02, orientation='vertical', description='a1', continuous_update=False)
m1 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=2., step=0.01, value=1.0, orientation='vertical', description='m1', continuous_update=False)
h1 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=2., step=0.01, value=0.1, orientation='vertical', description='h1', continuous_update=False)
a12 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=0.5, step=0.01, value=0.021, orientation='vertical', description='a12', continuous_update=False)
m12 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=2., step=0.01, value=1., orientation='vertical', description='m12', continuous_update=False)
a2 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=1., step=0.01, value=0.2, orientation='vertical', description='a2', continuous_update=False)
m2 = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=2., step=0.01, value=1.1, orientation='vertical', description='m2', continuous_update=False)
S1_init = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=2., step=0.01, value=1.0, orientation='vertical', description='t1_init', continuous_update=False)
S2_init = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0., max=2., step=0.01, value=1.0, orientation='vertical', description='t2_init', continuous_update=False)
df = initialize_df(pd.read_csv('data/data.csv', parse_dates=['Date'], dayfirst=True))
sliders = {
'a1': a1, 'm1': m1, 'h1': h1,
'a12': a12, 'm12': m12,
'a2': a2, 'm2': m2, 'S1_init': S1_init, 'S2_init': S2_init,
}
out = interactive_output(
plot_model,
sliders
)
display(HBox([a1, m1, h1, a12, m12, a2, m2, S1_init, S2_init]), out)
Examine Computational Performance#
Test the cycle time of the original function and compare to an updated (vectorized) function.
param_list = [('a1', 0.33),
('m1', 1.0),
('h1', 1.8),
('a12', 0.02),
('m12', 0.6),
('a2', 0.02),
('m2', 0.8),
('S1_init', 1.0),
('S2_init', 1.0)
]
params = {p[0]: max(0, np.random.normal(p[1])) for p in param_list}
# run some number of loops to generate an average execution time
times1, times2 = [], []
n_iterations = 10
for i in range(n_iterations):
t0 = time.time()
df = update_df()
t1 = time.time()
rain = df['Rain (mm/h)'].to_numpy()
evap = df['Evap (mm/h)'].to_numpy()
dt = df['dt_hours'].to_numpy()
s1, s2, q1, q2, q12, q_tot = update_states_vectorized(rain=rain, evap=evap, dt=dt, **params)
t2 = time.time()
times1.append(t1 - t0)
times2.append(t2 - t1)
mean1 = np.mean(times1)
mean2 = np.mean(times2)
print(f'Avg. of {n_iterations} iterations:')
print(f' update_df: {mean1:.2f}/loop')
print(f' update_df_update: {mean2:2f}/loop')
print(f'Vectorization speeds up computation ~{round(mean1/mean2, 0)}x')
Avg. of 10 iterations:
update_df: 1.84/loop
update_df_update: 0.036734/loop
Vectorization speeds up computation ~50.0x


 ]
]